Apache Kafka¶
What is Apache Kafka?¶
Apache Kafka is:
- distributed event streaming platform;
- open-source;
- used for:
- high-performance data pipelines;
- streaming analytics;
- data integration;
- mission-critical applications.
Apache Kafka properties¶
Apache Kafka properties:
- distribution — not one server, but many servers working together;
- fault tolerance;
- high availability;
- data consistency and availability — CA, see CAP theorem;
- high performance (bandwidth);
- horizontal scaling;
- integrability.
History of Apache Kafka¶
History of Apache Kafka:
- Developed by LinkedIn.
- Program code published in 2011.
- Member of the Apache Software Foundation since 2012.
- The product is developed in
ScalaandJavaprogramming languages.
What task does Apache Kafka solve¶
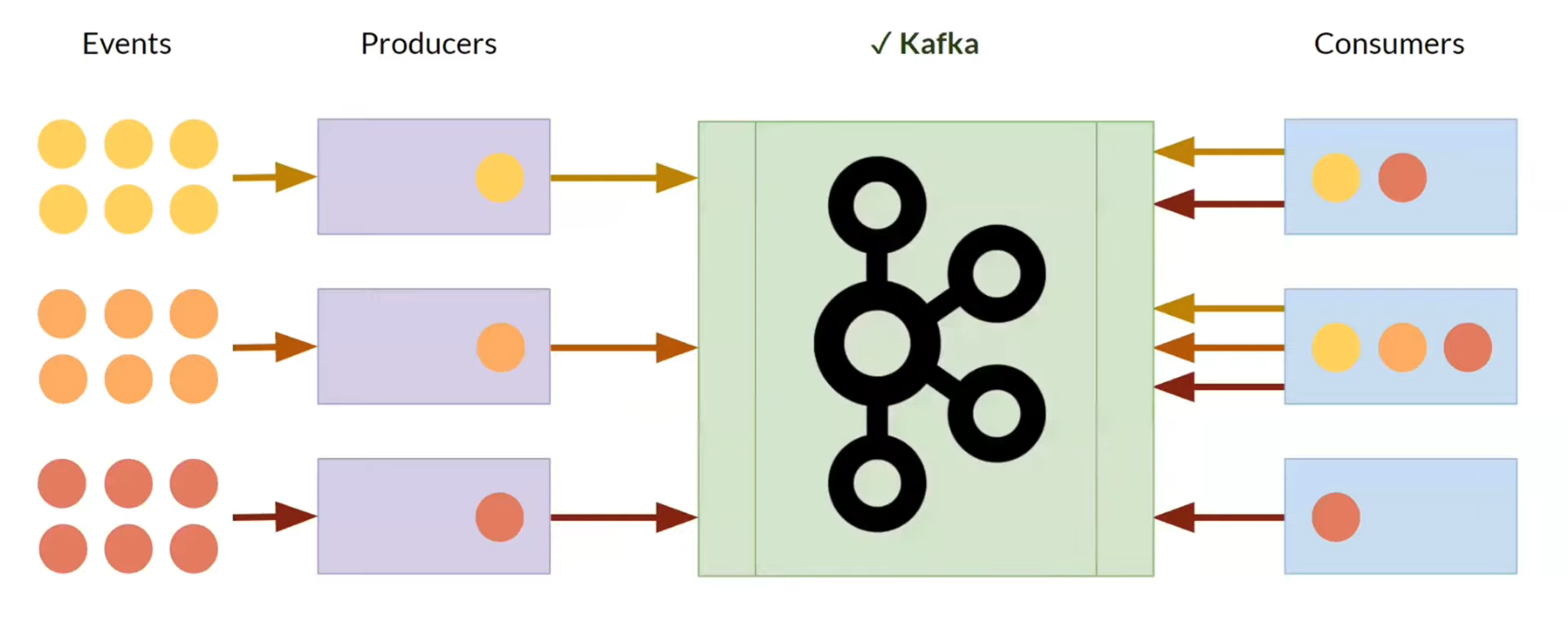
The main entities of Apache Kafka¶
Kafka Cluster: brings together several Kafka Brokers.Kafka Broker(Kafka Server | Kafka Node): receives, stores and issues messages.Zookeper:- Cluster status, configuration, address book (data).
- Selects Controller, provides consistency.
Kafka Message(Record | Event) —key-valuepair.Topic/Partition— stream of data.Producer.Consumer.
Message¶
| Message field | Description |
|---|---|
Key |
Key (optional). Used to distribute messages across the cluster. |
Value |
Message content, byte array. |
Timestamp |
Message time (from epoch). Set when sending or processing within the cluster. |
Headers |
A set of key-value pairs with custom message attributes. |
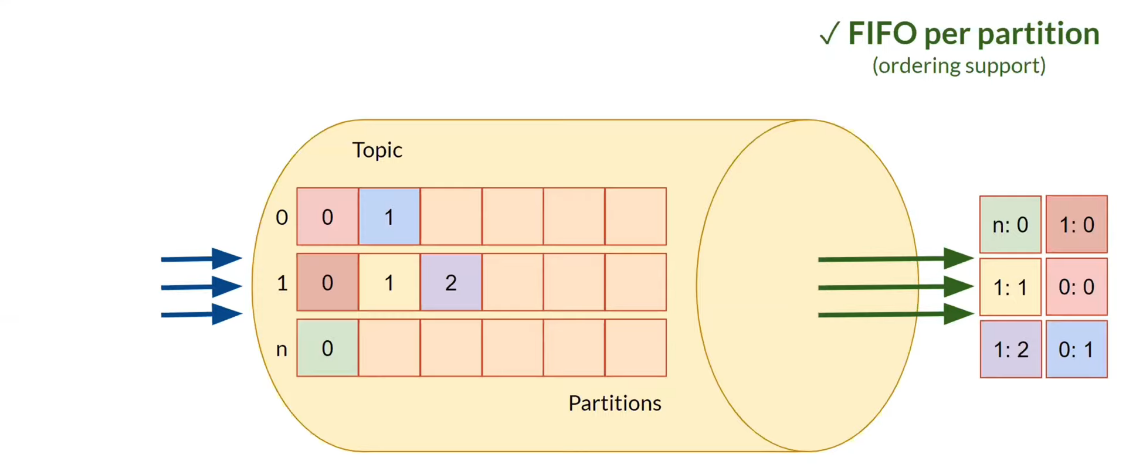
Topic / Partition¶
- Partitions are used to speed up reading and writing data (parallelization).
- Support for FIFO ordering at the partition level.
-
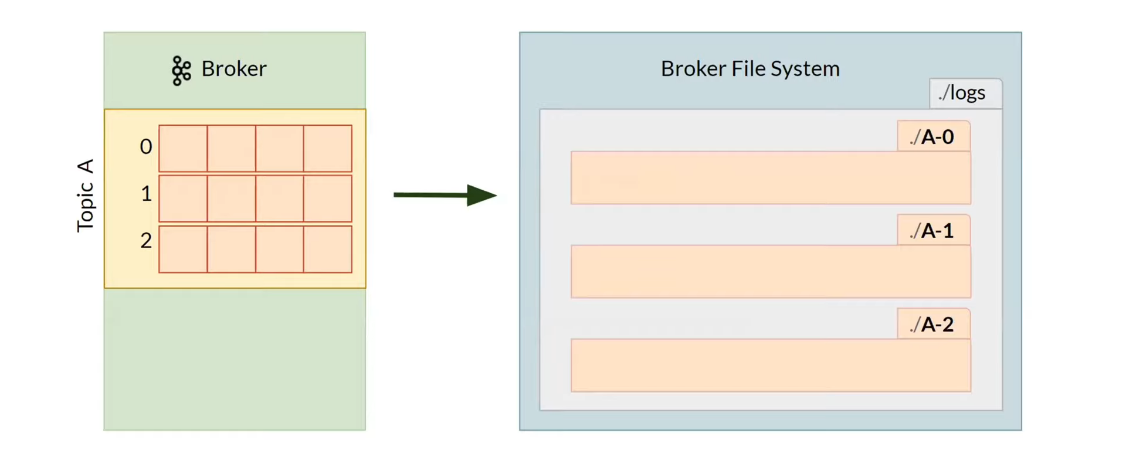
When reading from a topic, the data is not deleted.
-
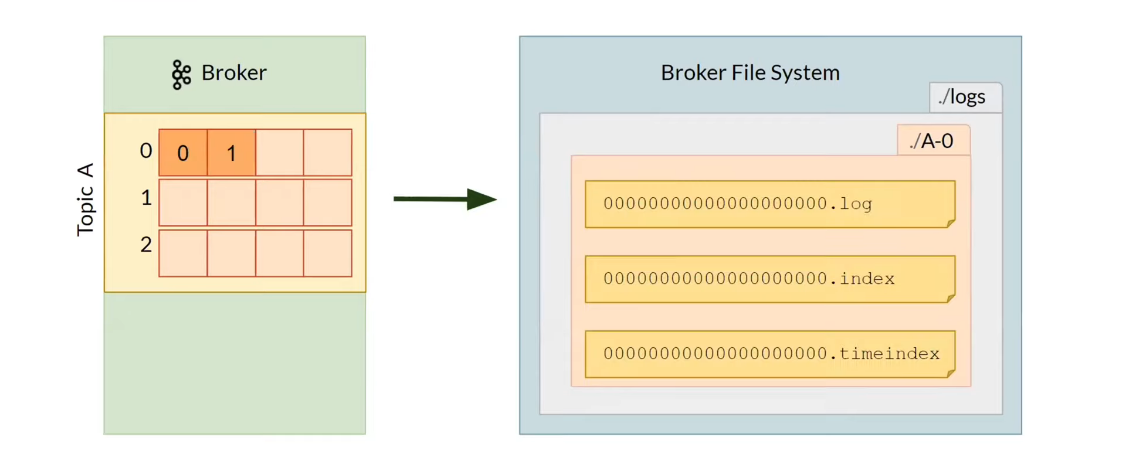
The data is stored in the Broker File System in log files.
-
Partition files:
-
Removing data from Apache Kafka Topic:
Warning
The delete operation from Apache Kafka Topic is not supported.
Tip
Supports automatic deletion of data after TTL.
Entire partition segments are deleted, not individual messages. Segment timestamp expired → to delete.
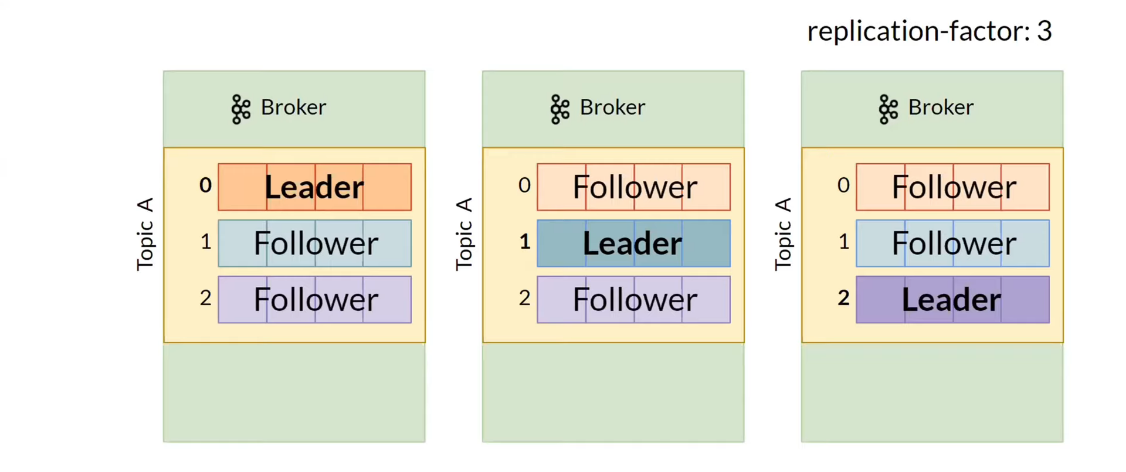
-
Set
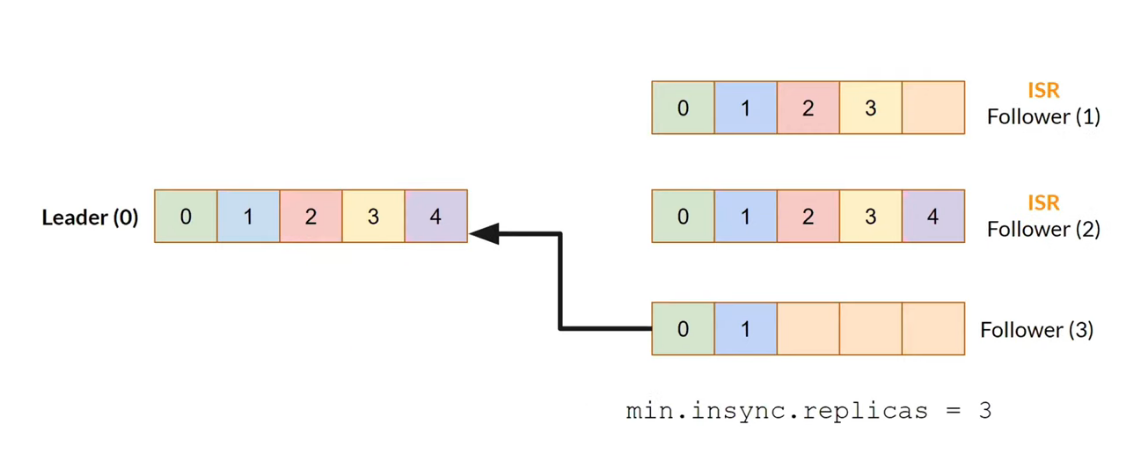
replication-factor> 1.- That is, for each partition there should be > 1 replica, and they should not be stored on one node.
Kafka ControllerassignsLeaderreplicas. Read and write operations are performed only on theLeaderreplica: produce → Leader → consume.- It is not recommended to host all
Leaderreplicas of topics on the same node. So she will be overloaded, and the rest nodes will be disabled.
-
Followersfetch data fromLeaderperiodically.- Synchronous recording from
LeadertoFollower. Therefore, the recording slows down a bit. - ISR
Followeris a reliable candidate forLeader. - Set
min.insync.replicas = 3. If there are not enoughLeader+ISR Followersonline, then a write error occurs.
- Synchronous recording from
Producer¶
acks— delivery guarantee parameter, can take the following values:0—Producerdoes not wait for confirmation of sending a message; the most unreliable mode, messages can be lost;1—Producerwaits for confirmation of sending a message only from theLeaderreplica; compromise mode, messages may be lost in some cases, for example, if a broker with aLeaderreplica falls before execution message replication; frequently used option;-1(all) —Producerwaits for confirmation of sending messages from all ISR replicas, includingLeader; most reliable option.
- Delivery semantic support:
at most once;at least once;exactly once(idempotence).
flowchart TD
title[<u>Producer send message flow diagram</u>]
title---A
style title fill:#FFF,stroke:#FFF
linkStyle 0 stroke:#FFF,stroke-width:0;
A["<b>Producer.send()</b>"<br/>message] --> B[fetch metadata];
B -. fetch .-> C[(Zookeper)];
C -. metadata .-> B;
B ---> D[serialize message];
D --> E[define partition];
E --> F[compress message];
F --> G[accumulate batch];
G --> H[Sending a message to the right brokers and partitions]Producer.send() message flow:
-
fetch metadatafromZookeperthrough a broker.- Gets the state of the cluster and topic placement.
- This operation will block
send()until the metadata has been received or the timeout is 60 seconds (default).
Note
It is not necessary to create a new
Producerfor every message sent. Use singleton instead. -
serialize messageto the desired format:key.serializer,value.serializer;- for example,
StringSerializer()— convert data into a byte array.
define partitionwhere the message will go:explicit partition— specify the partition manually;round-robin;key-defined(key_hash %n) — frequently used feature, used to record messages with the same key to the same partition; for example, log user messages with UUIDs.
- compress message;
- accumulate batch:
batch.size- by size;linger.ms- by timeout.
- Sending a message to the right brokers and partitions.
Consumer¶
flowchart TD
title[<u>Consumer poll messages flow diagram</u>]
title---A
style title fill:#FFF,stroke:#FFF
linkStyle 0 stroke:#FFF,stroke-width:0;
A["<b>Consumer.poll()</b>"<br/>messages] --> B[fetch metadata];
B -. fetch .-> C[(Zookeper)];
C -. metadata .-> B;
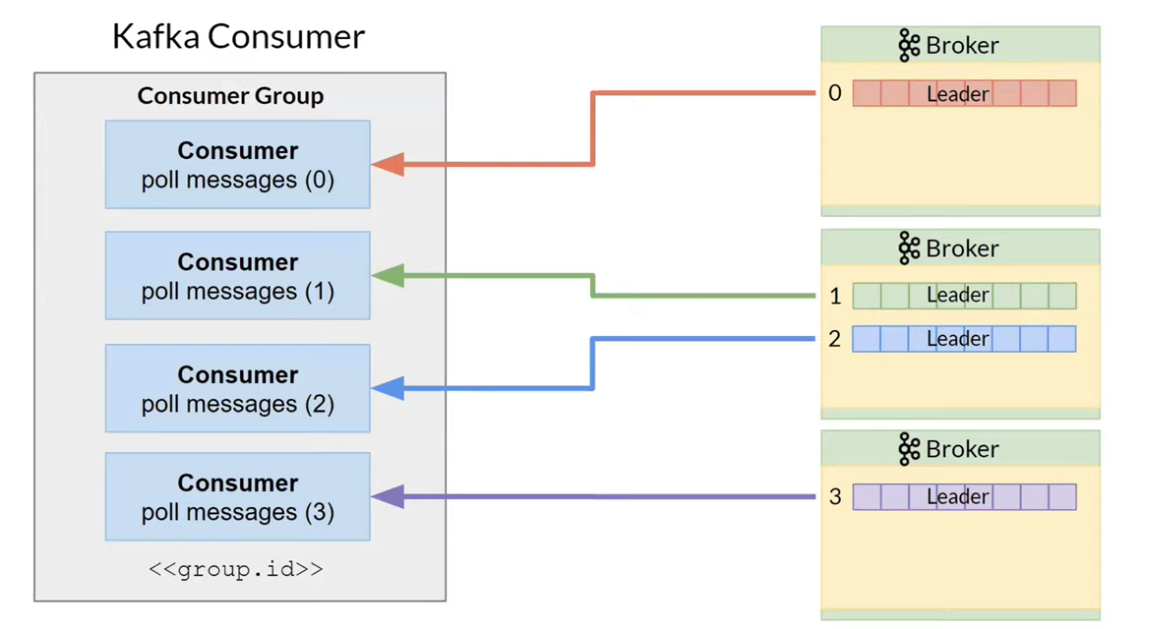
B ---> D[Connecting to Leader-replicas<br/>of all topic partitions];Single thread processing can be slow. To speed up, it is possible to combine several Consumer into Consumer Group.
The optimal design is when one Consumer reads data from one Topic.
Apache Kafka stores in a separate Topic named __consumer_offsets offsets for each Consumer Group and Partition:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
Partition |
A/0 |
Group |
X |
Offset |
2 |
Types of commits:
- Auto commit → at most once → risk of losing message when
Consumerfails after commit. - Manual commit → at least once → risk of receiving duplicate messages.
- Custom offset management → exactly once → not missed, no duplicates.
Consumer Group is inactive for a long time:
- max inactive period:
offsets.retention.minutes; - offsets deleted from
__consumer_offsets; - after group activatio →
auto.offset.reset:earliestorlatest.